An Individual Skeletal Muscle Is Separated From Adjacent Muscles by
As myotomedermatome cells migrate to assume adult. An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles by.

Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue And Organization Diagram Quizlet
An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of loose aerolar connective tissue called fascia.
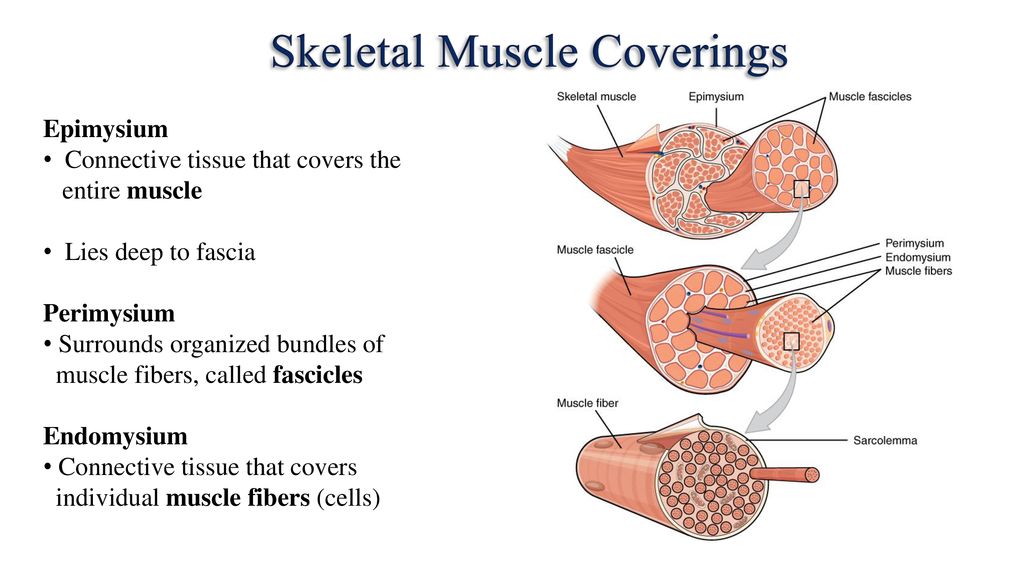
. An individual skeletal muscle separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of fibrous connective tissue called ___. Tendon is a cordlike or bandlike mass of dense connective tissue that connects a muscle to a bone. Attaching muscle to bone.
Bones muscles and tendons. - An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue called fascia. 41 rows An individual skeletal is separated from adjacent muscles by.
This connective tissue surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the end of its muscle fibers to form a cordlike tendon. It is comprised of 2 to 3 parallel collagen fiber bundles. Skeletal muscle tissue nervous tissue blood connective tissue.
Dense connective tissue called fascia fashe-ah separates an individual skeletal muscle from adjacent muscles and holds it in position. On plain radiographs muscles are characterized by a non-specific soft tissue density generally indistinguishable from adjacent soft tissues unless separated from them by fat. It is the thicker of the 2 subtypes that are normally easily separated from the underlying muscle layer.
An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue is called. Aponeuroses -fibrous sheets which may attach to bone or the coverings of adjacent. Unlike smooth muscle and cardiac muscle skeletal muscle.
Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Agriculture Food and Natural Resources. Muscular System Mastery Test Flashcards Quizlet 130 Chapter 7 skeletal system mastery test answer key. Tendon fascia surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the end of its muscle fibers to form a cord-like ___.
An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue called ____________. Skeletal muscle tissue nervous connective. CONNECTIVE TISSUE COVERINGS Fascia -separates individual skeletal muscle from adjacent muscles and holds in position by layers of dense connective tissue Tendon - made of dense regular connective tissue attaching muscle to bone.
Projects beyond the end to form cordlike tendon. Connective tissue forms broad fibrous sheets. How is an individual skeletal muscle separated from adjacent muscles.
It is composed of skeletal muscle tissue nervous tissue blood and other connective tissues. Tendon Fascia surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the end of its muscle fibers to form a cordlike tendon. Up to 24 cash back CONNECTIVE TISSUE COVERINGS.
Skeletal muscle serves many purposes including maintaining body posture moving the body and objects beginning the swallow reflex and changing thoracic volume to inhale or exhale. Connective Tissue Coverings Layers of connective tissue enclose and separate all parts of a skeletal muscle. Individual adult muscles are produced by merger of adjacent myotomes.
Also known as the epimysium this is the connective tissue sheath surrounding skeletal muscle and can in some cases connect directly to the periosteum of bones. Connective Tissue Coverings An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue called fascia fashe-ah. Up to 24 cash back Separate an individual skeletal muscle from adjacent muscles and hold it in position.
An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles and held in position by layers of dense connective tissue called fascia fashe-ah. Unlike the bones and tendons of the limb which are derived from the lateral plate mesoderm the limb musculature is formed from muscle precursors that originate in the hypaxial domain of the somites adjacent to the limb and migrate into the limb bud periphery where they meet the. Early in development nerves make connections with adjacent myotomes and dermatomes establishing a segmental innervation pattern.
Intertwine with those in a bones periosteum. A sheet of pearly white fibrous tissue that takes the place of a tendon in flat muscles having a wide area of attachment is called. By a layer of dense connective tissue called fascia Robert Lee Ph.
This connective tissue surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the end of its muscle fibers to. Layers of connective tissue extending into the muscle to form partitions between muscle bundles are continuous with attachments of muscle to periosteum called. An individual skeletal muscle is separated from adjacent muscles by.
Migrates to form skeletal muscles. This connective tissue surrounds each muscle and may project beyond the ends of its muscle fibers to form a cord-like tendon. On ultrasound skeletal muscles usually display a hypoechoic appearance with hyperechoic structures reflecting the interspersed perimysium.
Skeletal muscle is found throughout the body and functions to contract in response to a voluntary stimulus. Layers of connective. Continuous with outside layer of periosteum of bone.
Layers of dense connective tissue that separate and hold in position an individual skeletal muscle from adjacent muscles. Attach to the coverings of adjacent muscles. Three main tissues comprise the musculoskeletal unit.

Muscles And Muscle Tissue Part A Ppt Download

Muscles And Muscle Tissue Ppt Download

Chapter 9 Muscular System Anatomy Physiology Ivyanatomy Com Ppt Download
No comments for "An Individual Skeletal Muscle Is Separated From Adjacent Muscles by"
Post a Comment